UNI KROMA®
UNI KROMA® is an anatomical, fixed-bearing, unicompartmental prosthesis.
The tibial component is available in a metal-backed version (cemented or uncemented).
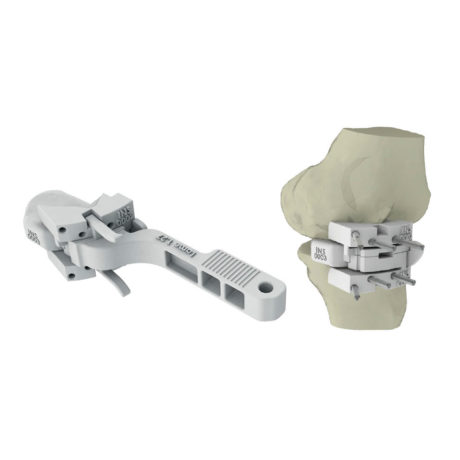
Fitting may be performed using a conventional technique or with custom instrumentation.
The instrumentation is original in that it is HYBRID.
Characteristics and materials
Characteristics :
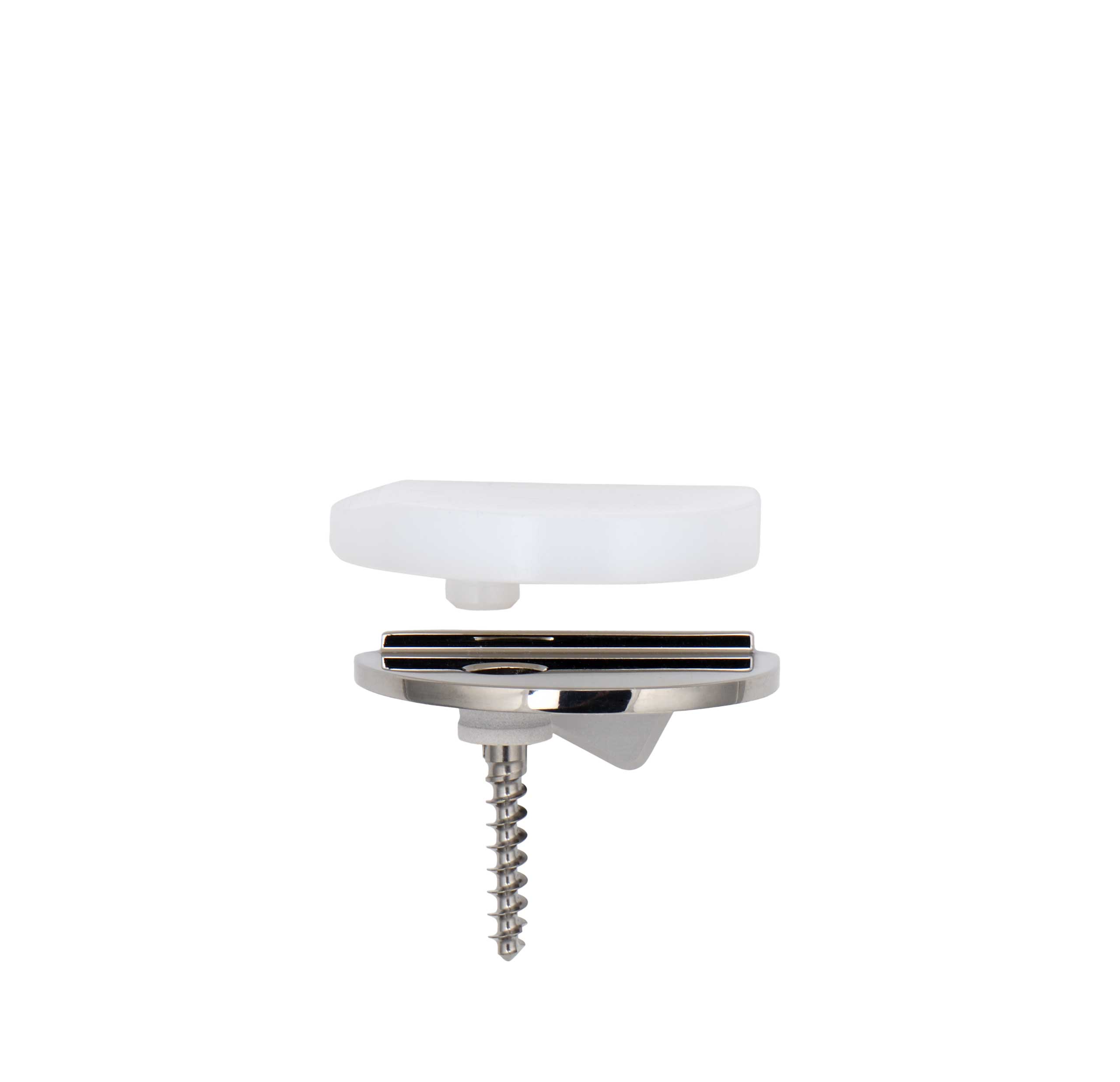
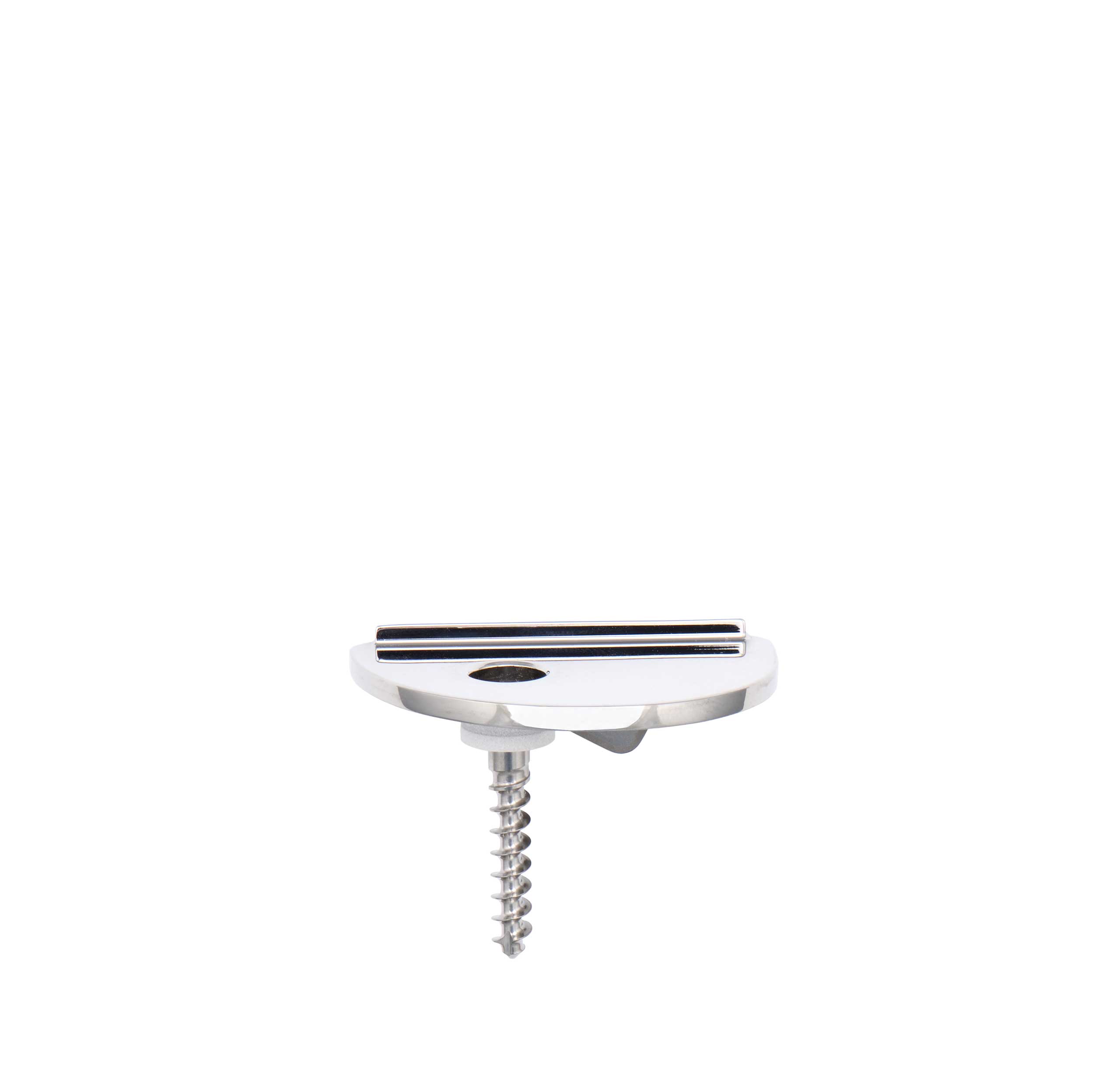
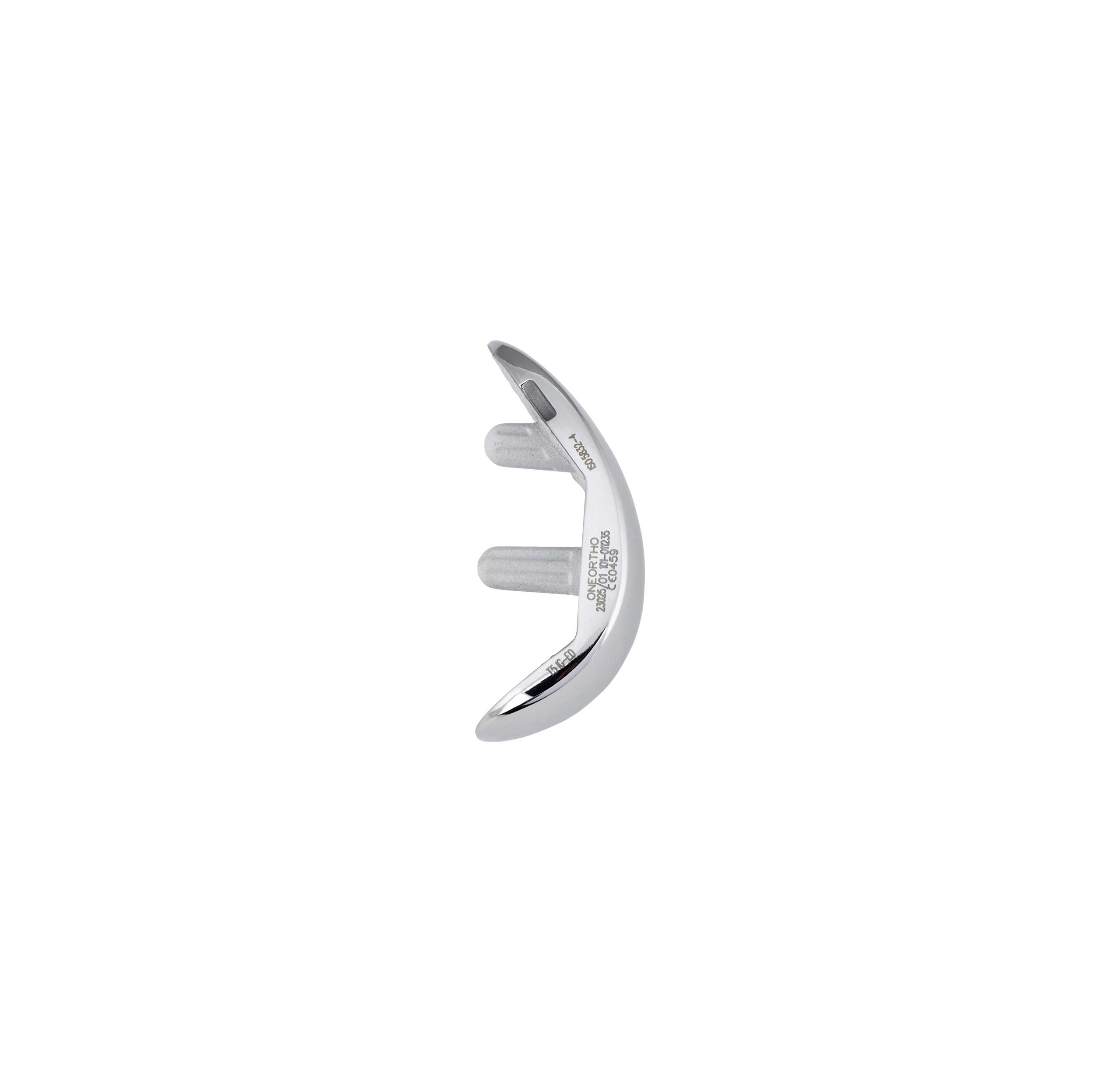
- The UNI KROMA® prosthesis is anatomical as it is comprised of a femoral component, a tibial baseplate and an insert which are asymmetrical: Internal Left/External Right or Internal Right/External Left.
- The femoral component and tibial baseplate are available in 6 sizes.
- The insert is available in 6 sizes and 4 thicknesses.
Materials :
- Cemented and cementless femoral component: Cobalt Chrome (CoCr) with dual coating for the cementless version (Titanium spray T40 + HA).
- Cementless tibial baseplate: Titanium (TA6V) with dual coating (Titanium spray T40 + HA).
- Cemented tibial baseplate: Cobalt Chrome (CoCr).
- Insert: Polyethylene.
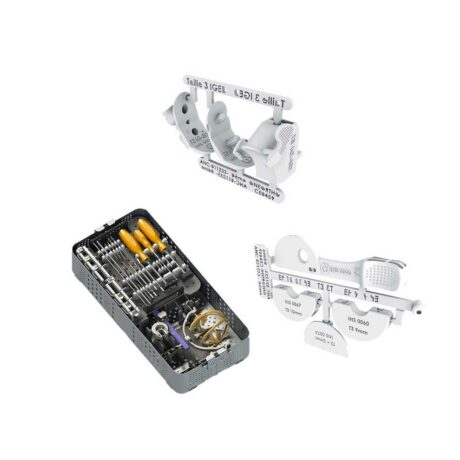
INSTRUMENTS
The instrumentation is called “hybrid” because it combines metallic parts and disposable polyamide parts (Single Use).
The technique of fitting with tailor-made instrumentation makes it possible to make the tibial cuts AND the distal femoral cut.
All UNI KROMA® instruments are manufactured by One Ortho Medical.
SERF is the exclusive distributor of these instruments.
Indications
The UNI KROMA® prosthesis is an unicompartmental prosthesis which is recommended in the following cases :
- Primary or secondary isolated osteoarthritis of the internal or external femorotibial compartment of the knee;
- Isolated necrosis of the internal or external condyle of the knee.
The prosthesis is indicated for patients whose bones have stopped growing.
Contraindications of the UNI KROMA® prosthesis are :
LOCAL :
- Inflammatory and microcrystalline rheumatoid damage ;
- Functional deficiencies of the cruciate and/or collateral ligaments ;
- Excessive fixed flexion or varus deformity ;
- Arthritic damage in the femoro‑tibial contro-lateral compartment ;
- Absence of the anterior cruciate ligament ;
- History of high tibial osteotomy.
GENERAL :
- Acute and chronic infectious diseases regardless of etiology and location ;
- Neuromuscular and psychiatric pathologies which can cause the failure of the fixation and postoperative care ;
- Inadequate or insufficient bone support not allowing proper anchoring of the prosthesis ;
- Physical activity ;
- Known allergy to one of the materials of the implant ;
- Pregnant women.